Research interest
My research mainly focuses on the impacts, life cycle, and track forecasting of tropical cyclones (TCs) over East Asia.
- Atmospheric and Climatic Impacts of Tropical Cyclones
- Tropical Cyclone Genesis and Dissipation Pathways
- Deep Learning for Tropical Cyclone Track Forecast
Atmospheric and Climatic Impacts of Tropical Cyclones
Rainfall
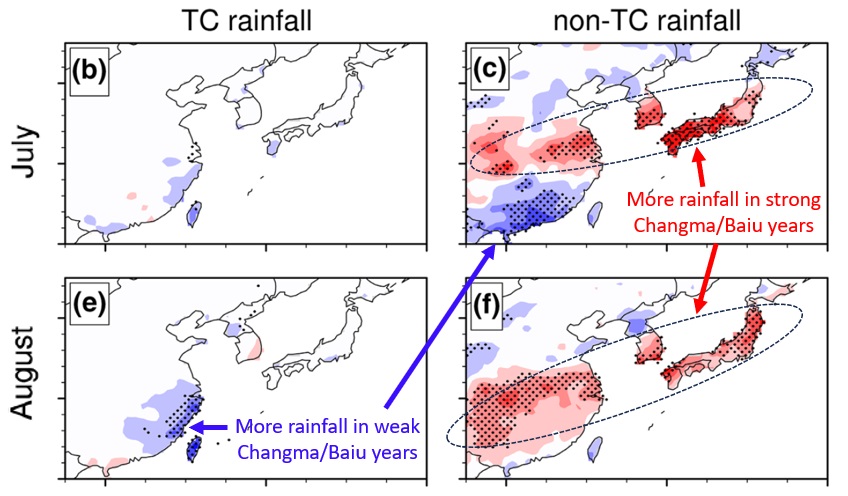
In addition to the East Asian Summer Monsoon, TCs are another major contributor to summer rainfall over East Asia, especially the coastal region. The variability of both TC-induced rainfall and monsoonal rainfall strongly modulates the hydrological cycle and related climate risk in the region. This study analyzes the contribution of TCs to the variability of summertime rainfall in the years of strong versus weak Changma/Baiu (the monsoon season in Korea/Japan). The possible large-scale driver of TC- and non-TC-induced rainfall variability is also examined.
Air pollution
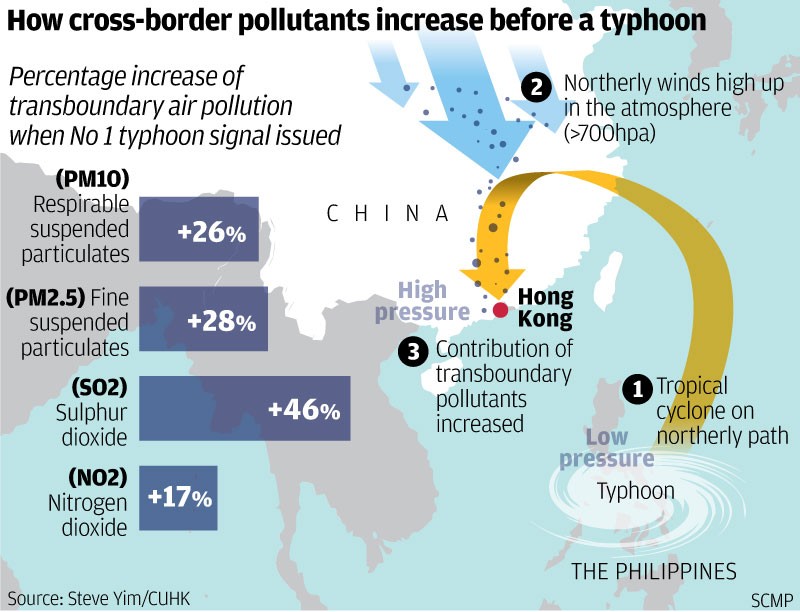
Numerous studies confirm that a TC near Luzon Strait or Taiwan can create favorable conditions for regional air pollutant episodes (light northerly for pollutant transport, subsidence unfavorable for pollutant dispersion, and increased insolation for enhanced photochemical reaction). These TC-induced episodes can cause higher pollutant concentrations than the others. Our study verifies the impact of TCs on local air quality in summer on a climate scale by investigating the influence of the change in the prevailing TC track over the western North Pacific.
Related articles:
- Cheung, H. M., Ho, C. H., Jhun, J. G., Park, D. S. R., & Yang, S. (2018). Tropical cyclone signals on rainfall distribution during strong vs. weak Changma/Baiu years. Climate Dynamics, 51, 2311-2320.
- Lam, Y. F., Cheung, H. M., & Ying, C. C. (2018). Impact of tropical cyclone track change on regional air quality. Science of the Total Environment, 610, 1347-1355.
- Zeng, S., Chu, J. E., Cheung, H. M., Baek, K., Kim, H. K., & Son, J. H. (2025). Seasonal Variations in PM2.5 levels in Hong Kong Induced by Eastern and Western Tropical Cyclones. Atmospheric Environment. 361, 121497.
Tropical Cyclone Genesis and Dissipation Pathways
Vortex Structure of Pre-existing Disturbances and Tropical Cyclogenesis
My research uses machine learning to classify the vertical vortex structures of the pre-existing disturbances that lead to tropical cyclone formation. We identified four distinct structures, finding that the vertical extent of a storm’s vorticity is a more critical factor for subsequent intensification than its magnitude.
Extratropical Transition of Tropical Cyclones: Pathways and Future Projections
When TCs move into the mid‑latitudes, they often transform from compact, warm‑core systems into expansive, cold‑core extratropical cyclones that affect much larger areas and populations. In our latest study, we analyzed 445 western North Pacific TCs and identified three objectively defined ET pathways—pinpointing which transitions are most common and which drive the highest post‑transition destructiveness.
In a separate line of work, we used a state‑of‑the‑art Earth system model to assess how elevated atmospheric CO₂ concentrations will reshape global ET activity and the destructiveness of transitioned storms under future‑climate scenarios. Also read this blog post 
Related articles:
- Cheung, H. M., & Chu, J. E. (2023). Global increase in destructive potential of extratropical transition events in response to greenhouse warming. npj Climate and Atmospheric Science, 6(1), 137.
- Cheung, H. M., Ho, C. H., & Chu, J. E. (2025). Extratropical transition pathways of tropical cyclones and their role in storm intensity and destructiveness. iScience, 28(7), 112814.
- Cheung, H. M., & Chu, J. E. (2025). Discernability of the Vertical Vortex Structure of Pre-existing Disturbances and Their Implication for Tropical Cyclone Formation. Weather and Climate Extremes. 50, 100804
Deep Learning for Tropical Cyclone Track Forecast
I developed a deep learning post-processing model to enhance the accuracy of medium-range tropical cyclone (TC) track forecasts (lead times > 5 days), supplementing traditional physical models. This model uses three classes of artificial neural networks to post-process and correct track errors from the Global Ensemble Forecast System (GEFS). The predictive skill was significantly improved through feature selection, hyperparameter tuning, and the application of shortcut connections.
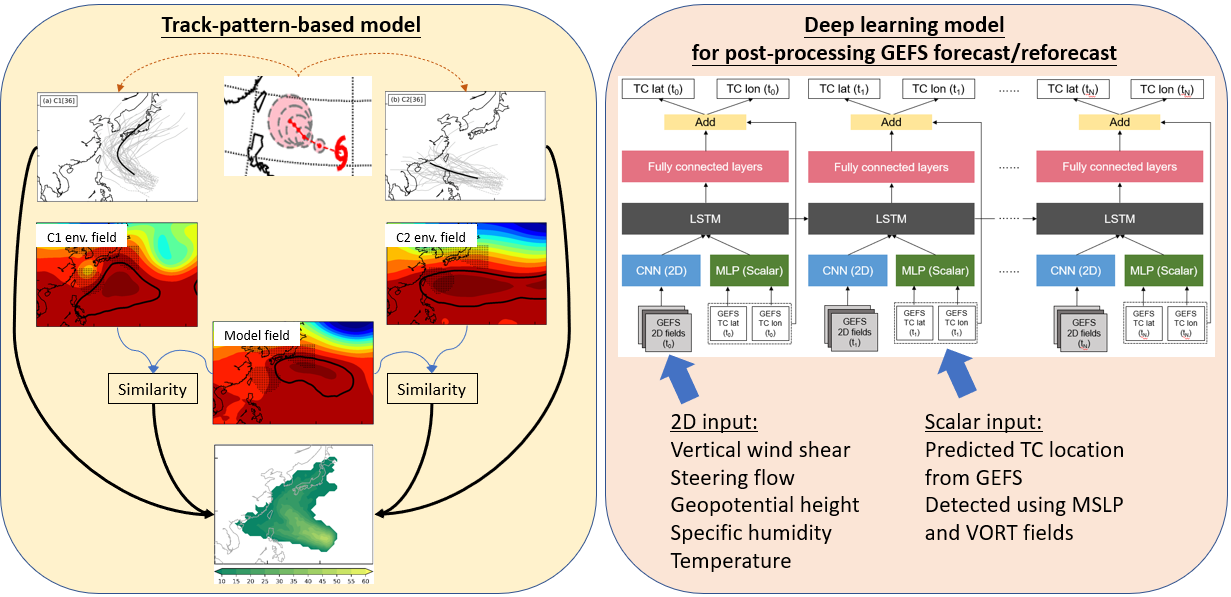
Related articles:
- Cheung, H. M., Ho, C. H., & Chang, M. (2022). Hybrid neural network models for postprocessing medium-range forecasts of tropical cyclone tracks over the western North Pacific. Artificial Intelligence for the Earth Systems, 1(4), e210003.
